
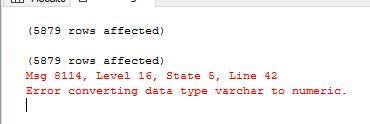
These digits are in a particular radix, or number base – i.e. Precision is an integer that represents the total number of digits allowed in this column. They are exact, and we define them by precision (p) and scale (s). SQL's exact numeric data types consist of NUMERIC(p,s) and DECIMAL(p,s) subtypes. Let's start our consideration of SQL numerical types with the exact or numeric data types. If this sounds confusing, rest assured that we'll explain it in detail later. Rather, they are an approximation of the real number because of the way that computer systems represent numbers. These represent real numbers, but they are not represented as exact numbers in the database. The approximate numeric data types are FLOAT(p), REAL, and DOUBLE PRECISION. Exact SQL numeric data type means that the value is stored as a literal representation of the number's value. The exact numeric data types are SMALLINT, INTEGER, BIGINT, NUMERIC(p,s), and DECIMAL(p,s). In SQL, numbers are defined as either exact or approximate. However, that's a topic for another article. You can compare character values in SQL, so one could argue that character values can also represent interval data. Ratio scales are very important in science.Įach SQL numeric data type is used to represent all of the above values, especially intervals and ratios.

If any of these have a zero value, there's nothing there. For example, think about mass, length, and duration. In a ratio scale, though, a zero value means there is nothing to be measured. Like an interval scale, a ratio has measurable differences between values.
Names would be stored in a character column. Each user has information in a name column and a phone number column. Data types tell your database what information to expect for that column. Once you've set up your table, you start listing column names and data types in SQL. You do this using DDL (Data Definition Language) statements like CREATE and DROP, which you can learn about in our Creating Tables in SQL course. We'll also examine some functions that convert data from one type to another.Ĭreating tables is the first step in any SQL coding project.

In this article, we will cover different variations of the SQL numeric data type. As you start on your learning path with, you will start to understand SQL's different data types. This data can take a couple of predefined formats. In addition, some internally used or deprecated types are available, but are not listed here.Working with databases of any kind means working with data. Most of the alternative names listed in the “ Aliases” column are the names used internally by PostgreSQL for historical reasons. Table 8.1 shows all the built-in general-purpose data types. Users can add new types to PostgreSQL using the CREATE TYPE command. PostgreSQL has a rich set of native data types available to users. Constructing Ranges and Multiranges 8.17.7. Built-in Range and Multirange Types 8.17.2. Composite Type Input and Output Syntax 8.17.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
